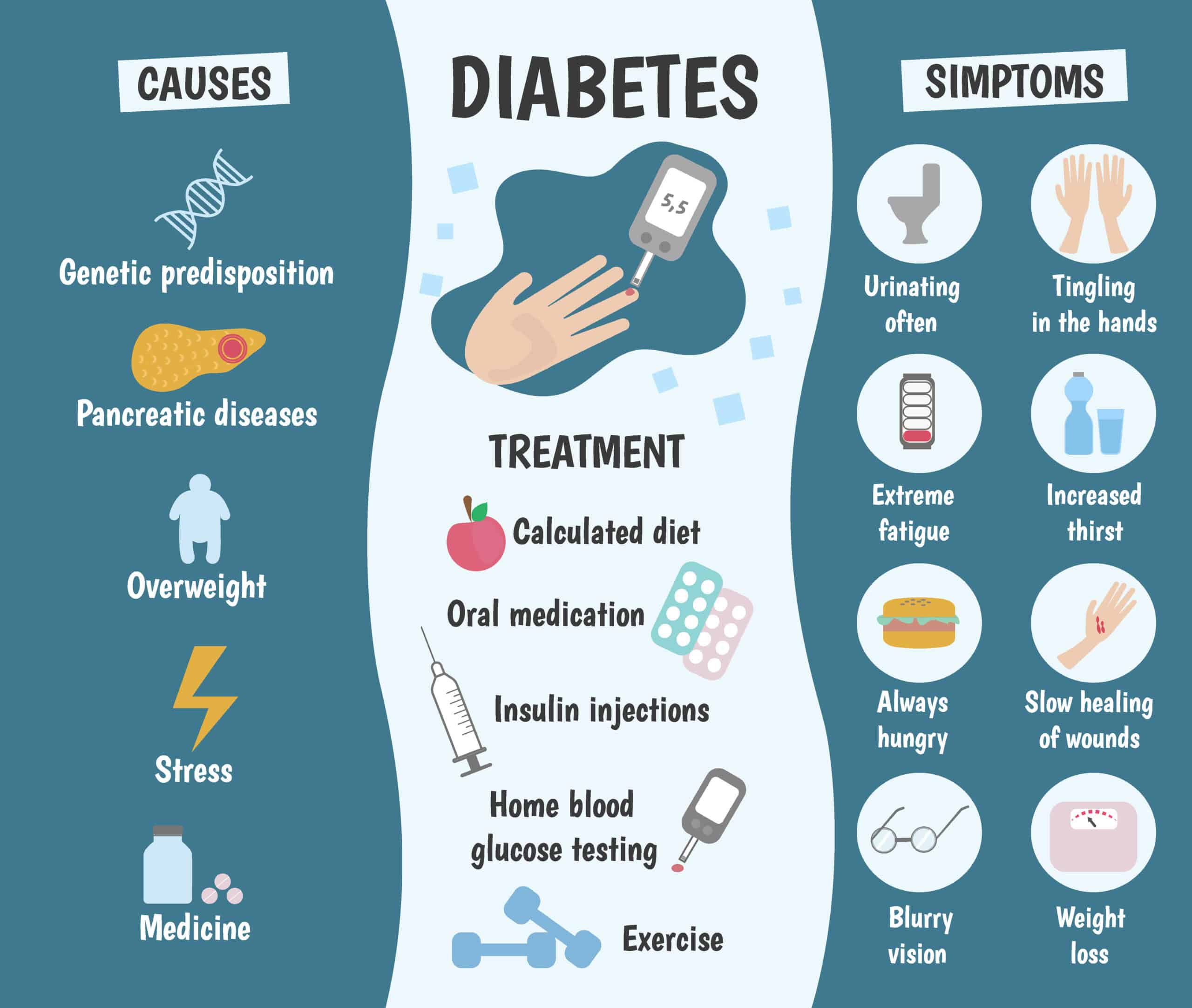
Diabetes Disease is one of the most common health conditions affecting millions of people worldwide today. In simple words, it happens when your body cannot properly use or produce insulin — a hormone that helps control blood sugar levels. Without balanced insulin, sugar builds up in the blood, which can lead to serious health problems over time.
Many people hear the term Diabetes Disease and immediately think it’s a life-ending condition. But the truth is, with the right lifestyle, treatment, and awareness, diabetes can be managed effectively. Millions of people around the world live active, healthy lives while managing this condition.
The rise in Diabetes Disease cases is mainly linked to modern lifestyle factors such as unhealthy diets, lack of exercise, stress, and genetics. This makes it not just a personal health challenge but also a global concern. The good news? Early diagnosis, proper treatment, and a healthy lifestyle can help prevent complications and allow people to lead normal lives.
| Type of Diabetes Disease | Description | Who is Affected | Management Approach |
|---|---|---|---|
| Type 1 Diabetes Disease | Body stops making insulin due to the immune system attacking insulin-producing cells. | Mostly children, teens, and young adults. | Requires daily insulin, healthy diet, and regular monitoring. |
| Type 2 Diabetes Disease | Body does not use insulin properly (insulin resistance). | Adults (common after age 40), but now also seen in younger people. | Lifestyle changes, oral medicines, insulin in some cases. |
| Gestational Diabetes Disease | High blood sugar that develops during pregnancy. | Pregnant women, usually goes away after childbirth. | Healthy diet, exercise, monitoring; sometimes medication. |
| Other Types (LADA, MODY) | Rare forms caused by genetic or autoimmune conditions. | Children, young adults, and those with family history. | Personalized medical care and ongoing monitoring. |
In this article, we’ll discuss how to reduce Diabetes Disease naturally and medically, including practical steps, diet plans, exercise routines, stress management, and medical support.

Understanding Diabetes Disease Before Reducing It
Diabetes occurs when the body either does not produce enough insulin or cannot use insulin effectively. This leads to high blood sugar (glucose) levels, which, over time, damage organs, nerves, and blood vessels.
- Type 1 Diabetes – Caused by autoimmune destruction of insulin-producing cells. It cannot be prevented, but it can be managed.
- Type 2 Diabetes – Mainly lifestyle-related and often preventable or reversible with healthy habits.
- Prediabetes – A stage where blood sugar is higher than normal but not yet diabetes. With lifestyle changes, prediabetes can be reversed.
1. Healthy Eating: The Foundation of Diabetes Disease Reduction

Diet plays the most important role in managing and reducing Diabetes Disease. A smart food plan helps maintain stable blood sugar levels.
Foods to Include:
- Whole Grains: Brown rice, oats, quinoa, and whole wheat.
- High-Fiber Foods: Vegetables, legumes, nuts, and seeds.
- Lean Proteins: Fish, eggs, paneer, tofu, chicken (grilled or boiled).
- Healthy Fats: Olive oil, avocado, almonds, walnuts.
- Low-GI Fruits: Apples, oranges, pears, and berries.
Foods to Avoid:
- Refined sugar and sugary drinks.
- White bread, white rice, and processed foods.
- Deep-fried snacks and fast foods.
- Excessive alcohol and packaged juices.
👉 Pro Tip: Instead of three heavy meals, eat smaller meals 5–6 times a day to keep blood sugar stable.
2. Physical Activity: Move to Improve Diabetes Disease
Exercise increases insulin sensitivity, meaning your body uses insulin more effectively.
Recommended Exercises:
- Walking or Jogging: 30–45 minutes daily.
- Strength Training: Weight lifting or resistance bands, at least 2–3 times a week.
- Yoga & Meditation: Improves both physical and mental well-being.
- Cycling or Swimming: Great for cardiovascular health.
👉 Pro Tip: Start slow if you’re not used to exercise. Even 10 minutes after every meal can significantly reduce sugar spikes.
3. Maintain a Healthy Weight
Obesity, especially belly fat, is one of the leading causes of insulin resistance. Even losing 5–10% of body weight can make a huge difference.
- Track your BMI (Body Mass Index) and waist circumference.
- Combine calorie control with regular workouts.
- Avoid fad diets; instead, focus on sustainable lifestyle changes.
4. Stay Hydrated
Drinking enough water helps regulate blood sugar by flushing out excess glucose through urine.
- Aim for 2–3 liters of water daily (depending on activity and climate).
- Replace sodas and sweetened drinks with water, green tea, or herbal tea.
5. Manage Stress and Sleep
Stress increases cortisol (a stress hormone), which can spike blood sugar levels. Similarly, poor sleep affects insulin function.
Stress Management Tips:
- Practice meditation or deep breathing for 10 minutes daily.
- Engage in hobbies like reading, gardening, or painting.
- Avoid overworking and maintain work-life balance.
Sleep Tips:
- Ensure 7–8 hours of quality sleep.
- Avoid late-night screen time.
- Maintain a regular sleep schedule.
6. Regular Monitoring of Blood Sugar
Keeping track of blood sugar helps in making timely adjustments to diet, exercise, and medication.
- Use a glucometer at home to monitor fasting and post-meal glucose levels.
- Get an HbA1c test every 3–6 months for long-term sugar control.
- Consult a doctor regularly for medical advice.
7. Medication and Medical Support
Sometimes lifestyle changes alone are not enough. Doctors may prescribe:
- Oral Medicines: To control blood sugar levels.
- Insulin Therapy: For those who cannot manage with tablets alone.
- Supplements: Vitamin D, Omega-3, and magnesium (if deficient).
👉 Never self-medicate. Always follow a doctor’s advice for safe and effective management.
8. Natural and Home Remedies for Diabetes Disease Control
Many natural foods and herbs help reduce blood sugar:
- Bitter Gourd (Karela): Improves insulin sensitivity.
- Fenugreek Seeds (Methi): Soak overnight and drink in the morning.
- Cinnamon: May improve insulin function.
- Amla (Indian Gooseberry): Rich in Vitamin C, supports pancreas health.
These remedies can complement medical treatment but should not replace prescribed medicines.
Note: Read Also – Today’s Major Medical and Health Updates in India
9. Preventing Diabetes in the Long Run
If you have prediabetes or a family history of diabetes, prevention is possible.
- Maintain a healthy lifestyle from a young age.
- Get regular check-ups if you are overweight or above 35 years.
- Educate family members about healthy eating and exercise.
10. Government and Community Support in India
The Indian government has introduced several programs to support diabetes prevention:
- Ayushman Bharat – Health & Wellness Centres offer free screenings.
- NPCDCS (National Programme for Prevention and Control of Diabetes, Cancer, Cardiovascular Diseases, and Stroke).
- Public health campaigns promoting fitness, yoga, and healthy eating.
Community awareness, early detection, and lifestyle education are crucial in controlling the diabetes epidemic.
Conclusion for Diabetes Disease
Diabetes does not have to control your life. With the right diet, exercise, weight management, stress control, and medical support, you can reduce diabetes and prevent complications. The key is consistency—small daily changes can lead to big long-term results.
Remember: Your health is in your hands. Start today with healthier choices, and you’ll be taking powerful steps toward reducing diabetes and living a longer, healthier life.